FATE ON Spark Deployment Guide¶
1.Server Information¶
| Server | |
|---|---|
| Number | >1 (Depending on user needs) |
| Specs | 8 core /16GB memory / 500GB hard disk/10M bandwidth |
| OS | CentOS linux 7.2 & above/Ubuntu 16.04 & above |
| Dependency | Please refer section 4.5 |
| User | user: app, user group: apps (app user should be able to execute sudo su root without password) |
| File System | 1. mount 500G hard disk to /data 2. make /data/projects directory, ownership to app:apps |
2.Cluster Information¶
| party | partyid | Host name | IP Address | OS | Software | Service |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PartyA | 10000 | VM-0-1-centos | 192.168.0.1 | CentOS 7.2/Ubuntu 16.04 | fate,mysql, nginx | fateflow,fateboard,mysql,nginx |
| PartyA | 10000 | Spark、HDFS | ||||
| PartyA | 10000 | RabbitMQ or pulsar | ||||
| PartyB | 9999 | VM-0-2-centos | 192.168.0.2 | CentOS 7.2/Ubuntu 16.04 | fate,mysql, nginx | fateflow,fateboard,mysql,nginx |
| PartyB | 9999 | Spark、HDFS | ||||
| PartyB | 9999 | RabbitMQ or pulsar |
Architecture:
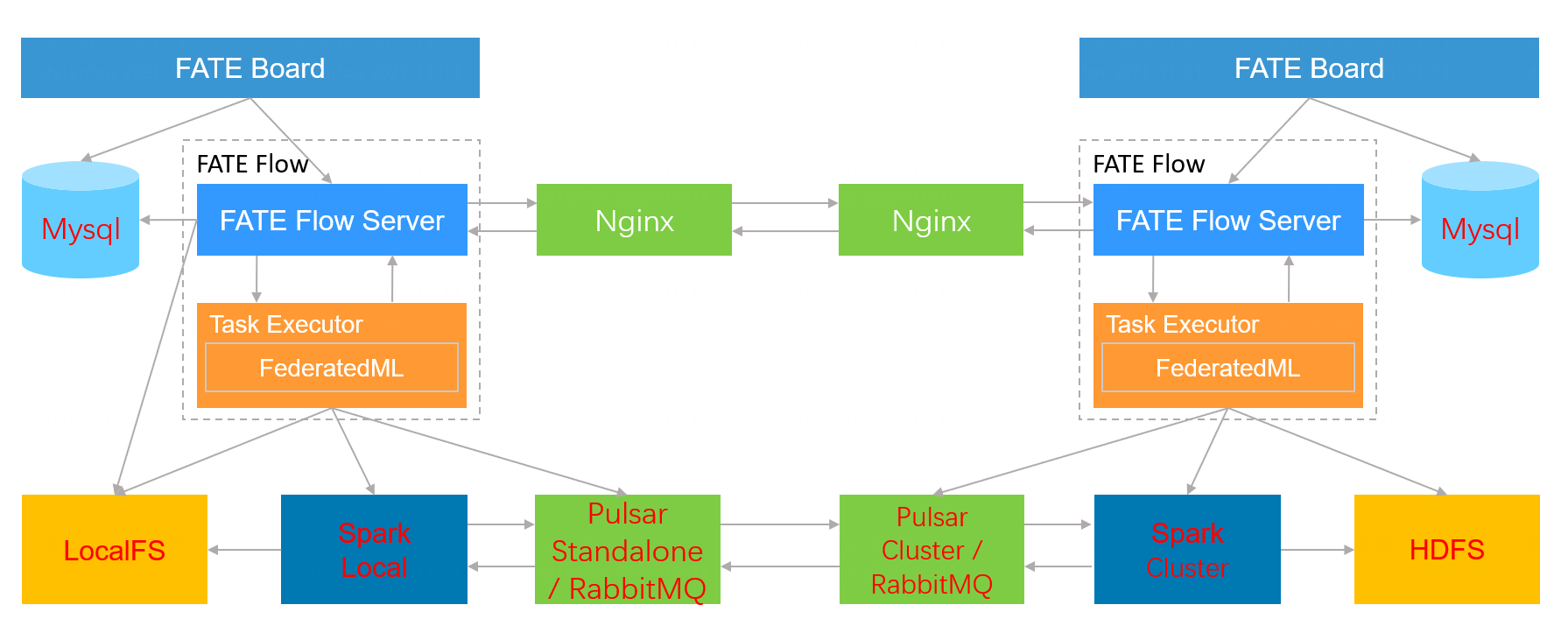 |
|---|
3.Module Information¶
| Product | Module | Port | Information |
|---|---|---|---|
| fate | fate_flow | 9360;9380 | Manages workflow of federated learning jobs, one service instance per party |
| fate | fateboard | 8080 | Visualizes federated learning process, one service instance per party |
| nginx | nginx | 9370 | proxy for cross-party scheduling |
| mysql | mysql | 3306 | meta table storage |
| Spark | compute engine | ||
| HDFS | storage engine | ||
| RabbitMQ(or Pulsar) | proxy for cross-party data exchange |
4. Basic Environment Configuration¶
4.1 hostname configuration (optional)¶
1) Modify the hostname
Execute under 192.168.0.1 root user:
hostnamectl set-hostname VM-0-1-centos
Execute under 192.168.0.2 root user:
hostnamectl set-hostname VM-0-2-centos
2) Add the host mapping
Execute under the target server (192.168.0.1 192.168.0.2) root user:
vim /etc/hosts
192.168.0.1 VM-0-1-centos
192.168.0.2 VM-0-2-centos
4.2 Shut down SELinux (optional)¶
Execute under the root user of the target server (192.168.0.1 192.168.0.2):
Confirm if SELinux is installed
CentOS system executes.
rpm -qa | grep selinux
For Ubuntu systems, run
apt list --installed | grep selinux
If SELinux is already installed, do the following.
setenforce 0
4.3 Modifying Linux system parameters¶
Execute under the root user on the target server (192.168.0.1 192.168.0.2 192.168.0.3):
vim /etc/security/limits.conf
* soft nofile 65536
* hard nofile 65536
vim /etc/security/limits.d/20-nproc.conf
* soft nproc unlimited
4.4 Turn off the firewall (optional)¶
** Execute under the root user of the target server (192.168.0.1 192.168.0.2 192.168.0.3) **
In case of CentOS system.
systemctl disable firewalld.service
systemctl stop firewalld.service
systemctl status firewalld.service
If it is an Ubuntu system.
ufw disable
ufw status
4.5 Software environment initialization¶
Execute under the root user of the target server (192.168.0.1 192.168.0.2 192.168.0.3)
1) Create user
groupadd -g 6000 apps
useradd -s /bin/bash -g apps -d /home/app app
passwd app
2) Create a directory
mkdir -p /data/projects/fate
mkdir -p /data/projects/install
chown -R app:apps /data/projects
3) Install dependencies
#centos
yum -y install gcc gcc-c++ make openssl-devel gmp-devel mpfr-devel libmpc-devel libaio numactl autoconf automake libtool libffi-devel snappy snappy -devel zlib zlib-devel bzip2 bzip2-devel lz4-devel libasan lsof sysstat telnet psmisc
#ubuntu
apt-get install -y gcc g++ make openssl supervisor libgmp-dev libmpfr-dev libmpc-dev libaio1 libaio-dev numactl autoconf automake libtool libffi- dev libssl1.0.0 libssl-dev liblz4-1 liblz4-dev liblz4-1-dbg liblz4-tool zlib1g zlib1g-dbg zlib1g-dev
cd /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu
if [ ! -f "libssl.so.10" ];then
ln -s libssl.so.1.0.0 libssl.so.10
ln -s libcrypto.so.1.0.0 libcrypto.so.10
fi
5. Deploy dependent components¶
Note: The default installation directory for this guide is /data/projects/install, and the execution user is app, modify it according to the specific situation when installing.
5.1 Get the installation package¶
Execute on the target server (192.168.0.1 with extranet environment) under the app user:
mkdir -p /data/projects/install
cd /data/projects/install
wget https://webank-ai-1251170195.cos.ap-guangzhou.myqcloud.com/resources/Miniconda3-py38_4.12.0-Linux-x86_64.sh
wget https://webank-ai-1251170195.cos.ap-guangzhou.myqcloud.com/resources/jdk-8u345.tar.xz
wget https://webank-ai-1251170195.cos.ap-guangzhou.myqcloud.com/resources/mysql-fate-8.0.28.tar.gz
wget https://webank-ai-1251170195.cos.ap-guangzhou.myqcloud.com/resources/openresty-1.17.8.2.tar.gz
wget https://webank-ai-1251170195.cos.ap-guangzhou.myqcloud.com/fate/${version}/release/pip_packages_fate_${version}.tar.gz
wget https://webank-ai-1251170195.cos.ap-guangzhou.myqcloud.com/fate/${version}/release/fate_install_${version}_release.tar.gz
#transfer to 192.168.0.1 and 192.168.0.2
scp *.tar.gz app@192.168.0.1:/data/projects/install
scp *.tar.gz app@192.168.0.2:/data/projects/install
5.2 Operating system parameter checking¶
execute under the target server (192.168.0.1 192.168.0.2 192.168.0.3) app user
# of file handles, not less than 65535, if not meet the need to refer to section 4.3 reset
ulimit -n
65535
#Number of user processes, not less than 64000, if not, you need to refer to section 4.3 to reset
ulimit -u
65535
5.3 Deploying MySQL¶
Execute under the target server (192.168.0.1 192.168.0.2) app user
1) MySQL installation:
# Create mysql root directory
mkdir -p /data/projects/fate/common/mysql
mkdir -p /data/projects/fate/data/mysql
#Unpack the package
cd /data/projects/install
tar xf mysql-*.tar.gz
cd mysql
tar xf mysql-8.0.28.tar.gz -C /data/projects/fate/common/mysql
#Configuration settings
mkdir -p /data/projects/fate/common/mysql/mysql-8.0.28/{conf,run,logs}
cp service.sh /data/projects/fate/common/mysql/mysql-8.0.28/
cp my.cnf /data/projects/fate/common/mysql/mysql-8.0.28/conf
#initialize
cd /data/projects/fate/common/mysql/mysql-8.0.28/
./bin/mysqld --initialize --user=app --basedir=/data/projects/fate/common/mysql/mysql-8.0.28 --datadir=/data/projects/fate/data/mysql > logs/init.log 2>&1
cat logs/init.log |grep root@localhost
#Note that the output message after root@localhost: is the initial password of the mysql user root, which needs to be recorded and used to change the password later
#Start the service
cd /data/projects/fate/common/mysql/mysql-8.0.28/
nohup ./bin/mysqld_safe --defaults-file=./conf/my.cnf --user=app >>logs/mysqld.log 2>&1 &
#change mysql root user password
cd /data/projects/fate/common/mysql/mysql-8.0.28/
./bin/mysqladmin -h 127.0.0.1 -P 3306 -S ./run/mysql.sock -u root -p password "fate_dev"
Enter Password: [Enter root initial password]
#Verify login
cd /data/projects/fate/common/mysql/mysql-8.0.28/
./bin/mysql -u root -p -S ./run/mysql.sock
Enter Password: [Enter root modified password:fate_dev]
2) Build authorization and business configuration
cd /data/projects/fate/common/mysql/mysql-8.0.28/
./bin/mysql -u root -p -S ./run/mysql.sock
Enter Password:[fate_dev]
# Create the fate_flow library
mysql>CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS fate_flow;
#Create remote user and authorization
1) 192.168.0.1 execute
mysql>CREATE USER 'fate'@'192.168.0.1' IDENTIFIED BY 'fate_dev';
mysql>GRANT ALL ON *. * TO 'fate'@'192.168.0.1';
mysql>flush privileges;
2) 192.168.0.2 execute
mysql>CREATE USER 'rate'@'192.168.0.2' IDENTIFIED BY 'rate_dev';
mysql>GRANT ALL ON *. * TO 'fate'@'192.168.0.2';
mysql>flush privileges;
# verify
mysql>select User,Host from mysql.user;
mysql>show databases;
5.4 Deploying the JDK¶
execute under the target server (192.168.0.1 192.168.0.2) app user:
#Create the jdk installation directory
mkdir -p /data/projects/fate/common/jdk
#Uncompress
cd /data/projects/install
tar xJf jdk-8u345.tar.xz -C /data/projects/fate/common/jdk
5.5 Deploying python¶
execute under the target server (192.168.0.1 192.168.0.2) app user:
#Create the python virtualization installation directory
mkdir -p /data/projects/fate/common/python
#Install miniconda3
cd /data/projects/install
tar xvf python-env-*.tar.gz
cd python-env
bash miniconda3-4.5.4-Linux-x86_64.sh -b -p /data/projects/fate/common/miniconda3
#Create a virtualized environment
/data/projects/fate/common/miniconda3/bin/python3.8 -m venv /data/projects/fate/common/python/venv
5.6 Deploy Spark & HDFS¶
See the deployment guide:Hadoop+Spark deployment
5.7 Deploying Nginx¶
See the deployment guide:Nginx deployment
5.8 Deploying RabbitMQ (or Pulsar)¶
See the deployment guide: RabbitMQ_deployment
See the deployment guide: Pulsar deployment
6 Deploying FATE¶
6.1 Software deployment¶
## Deploy the software
## On the target server (192.168.0.1 192.168.0.2) under the app user execute:
cd /data/projects/install
tar xf fate_install_*.tar.gz
cd fate_install_*
cp fate.env /data/projects/fate/
cp RELEASE.md /data/projects/fate/
tar xvf bin.tar.gz -C /data/projects/fate/
tar xvf conf.tar.gz -C /data/projects/fate/
tar xvf deploy.tar.gz -C /data/projects/fate/
tar xvf examples.tar.gz -C /data/projects/fate/
tar xvf fate.tar.gz -C /data/projects/fate/
tar xvf fateflow.tar.gz -C /data/projects/fate/
tar xvf fateboard.tar.gz -C /data/projects/fate
tar xvf proxy.tar.gz -C /data/projects/fate
# Set the environment variable file
#Execute on the target server (192.168.0.1 192.168.0.2) under the app user:
cat >/data/projects/fate/bin/init_env.sh <<EOF
fate_project_base=/data/projects/fate
export FATE_PROJECT_BASE=\$fate_project_base
export FATE_DEPLOY_BASE=\$fate_project_base
export PYTHONPATH=/data/projects/fate/fateflow/python:/data/projects/fate/fate/python
venv=/data/projects/fate/common/python/venv
export JAVA_HOME=/data/projects/fate/common/jdk/jdk-8u345
export PATH=\$PATH:\$JAVA_HOME/bin
source \${venv}/bin/activate
export FATE_LOG_LEVEL=DEBUG
export FATE_PROFILE_LOG_ENABLED=0
EOF
#Install dependencies
cd /data/projects/install
tar xvf pip_packages_fate_*.tar.gz
source /data/projects/fate/common/python/venv/bin/activate
cd pip_packages_fate_*
pip install -r /data/projects/fate/fate/python/requirements.txt -f ./ --no-index
cd /data/projects/fate/fate/python/fate_client
python setup.py install
cd /data/projects/fate/fate/python/fate_test
python setup.py install
pip list | wc -l
6.2 FATE-Board configuration file modification¶
1) conf/application.properties
- Service port
server.port --- default
- access url of fateflow
fateflow.url, host: http://192.168.0.1:9380, guest: http://192.168.0.2:9380
#Modify and execute under the target server (192.168.0.1) app user
cat > /data/projects/fate/fateboard/conf/application.properties <<EOF
server.port=8080
fateflow.url=http://192.168.0.1:9380
#priority is higher than {fateflow.url}, split by ;
fateflow.url-list=
fateflow.http_app_key=
fateflow.http_secret_key=
spring.http.encoding.charset=UTF-8
spring.http.encoding.enabled=true
server.tomcat.uri-encoding=UTF-8
fateboard.front_end.cors=false
fateboard.front_end.url=http://localhost:8028
server.tomcat.max-threads=1000
server.tomcat.max-connections=20000
spring.servlet.multipart.max-file-size=10MB
spring.servlet.multipart.max-request-size=100MB
spring.servlet.session.timeout=1800s
server.compression.enabled=true
server.compression.mime-types=application/json,application/xml,text/html,text/xml,text/plain
server.board.login.username=admin
server.board.login.password=admin
#only [h,m,s] is available
server.servlet.session.timeout=4h
server.servlet.session.cookie.max-age=4h
management.endpoints.web.exposure.exclude=*
feign.client.config.default.connectTimeout=10000
feign.client.config.default.readTimeout=10000
EOF
#Modify and execute under the target server (192.168.0.2) app user
cat > /data/projects/fate/fateboard/conf/application.properties <<EOF
server.port=8080
fateflow.url=http://192.168.0.2:9380
#priority is higher than {fateflow.url}, split by ;
fateflow.url-list=
fateflow.http_app_key=
fateflow.http_secret_key=
spring.http.encoding.charset=UTF-8
spring.http.encoding.enabled=true
server.tomcat.uri-encoding=UTF-8
fateboard.front_end.cors=false
fateboard.front_end.url=http://localhost:8028
server.tomcat.max-threads=1000
server.tomcat.max-connections=20000
spring.servlet.multipart.max-file-size=10MB
spring.servlet.multipart.max-request-size=100MB
spring.servlet.session.timeout=1800s
server.compression.enabled=true
server.compression.mime-types=application/json,application/xml,text/html,text/xml,text/plain
server.board.login.username=admin
server.board.login.password=admin
#only [h,m,s] is available
server.servlet.session.timeout=4h
server.servlet.session.cookie.max-age=4h
management.endpoints.web.exposure.exclude=*
feign.client.config.default.connectTimeout=10000
feign.client.config.default.readTimeout=10000
EOF
6.3 FATE configuration file modification¶
Configuration file: /data/projects/fate/conf/service_conf.yaml
6.3.1 running configuration¶
- FATE engine related configuration.
default_engines:
compute: spark
federation: rabbitmq #(or pulsar)
storage: HDFS
-
Listening ip, port of FATE-Flow
-
Listening ip, port of FATE-Board
-
db's connection ip, port, account and password
- Proxy related configuration (ip and port)
conf/service_conf.yaml
fateflow.
proxy: nginx
fate_on_spark:
nginx:
Host: 127.0.0.1
port: 9390
6.3.2 Dependent service configuration¶
conf/service_conf.yaml
fate_on_spark:
spark:
home:
cores_per_node: 40
nodes: 1
hdfs:
name_node: hdfs://fate-cluster
path_prefix:
# rabbitmq and pulsar
rabbitmq:
host: 127.0.0.1
mng_port: 12345
port. 5672
user: fate
password: fate
route_table:
pulsar:
host: 127.0.0.1
port. 6650
mng_port: 8080
cluster: standalone
tenant: fl-tenant
topic_ttl: 5
route_table:
-
HDFS-related configuration
- name_node is the full address of the hdfs namenode
- path_prefix is the default storage path prefix, if not configured then the default is /.
-
RabbitMQ related configuration
- host: host_ip
- management_port:
- mng_port: Management port
- port. Service port
- user: admin user
- password: administrator password
- route_table: Routing table information, default is empty
-
pulsar-related configuration
- host: host ip
- port: brokerServicePort
- mng_port: webServicePort
- cluster: cluster or standalone
- tenant: partner needs to use the same tenant
- topic_ttl: recycling resource parameter
- route_table: Routing table information, default is empty.
6.3.3 spark dependency distribution model(Only for Spark Cluster)¶
- "conf/service_conf.yaml"
dependent_distribution: true # Recommended to use true
Note:If this configuration is "true", the following actions can be ignored.
-
Dependency preparation:copy the entire fate directory to each working node, keeping the directory structure consistent
-
spark configuration modification: spark/conf/spark-env.sh ```shell script export PYSPARK_PYTHON=/data/projects/fate/common/python/venv/bin/python export PYSPARK_DRIVER_PYTHON=/data/projects/fate/common/python/venv/bin/python
##### 6.3.4 Reference configuration The configuration file format must be configured in yaml format, otherwise, an error will be reported when parsing, you can refer to the following example to configure manually, or use the following instructions to complete.
Modify and execute under the target server (192.168.0.1) app user¶
cat > /data/projects/fate/conf/service_conf.yaml <<EOF use_registry: false use_deserialize_safe_module: false dependent_distribution: false encrypt_password: false encrypt_module: fate_arch.common.encrypt_utils#pwdecrypt private_key: party_id: hook_module: client_authentication: fate_flow.hook.flow.client_authentication site_authentication: fate_flow.hook.flow.site_authentication permission: fate_flow.hook.flow.permission hook_server_name: authentication: client: switch: false http_app_key: http_secret_key: site: switch: false permission: switch: false component: false dataset: false fateflow: host: 192.168.0.1 http_port: 9380 grpc_port: 9360 nginx: host: http_port: grpc_port: proxy: nginx protocol: default database: name: fate_flow user: fate passwd: fate_dev host: 192.168.0.1 port: 3306 max_connections: 100 stale_timeout: 30 zookeeper: hosts: - 127.0.0.1:2181 use_acl: false user: fate password: fate default_engines: computing: spark federation: pulsar storage: localfs fate_on_standalone: standalone: cores_per_node: 20 nodes: 1 fate_on_eggroll: clustermanager: cores_per_node: 16 nodes: 1 rollsite: host: 127.0.0.1 port: 9370 fate_on_spark: spark: home: cores_per_node: 20 nodes: 1 linkis_spark: cores_per_node: 20 nodes: 2 host: 127.0.0.1 port: 9001 token_code: MLSS python_path: /data/projects/fate/python hive: host: 127.0.0.1 port: 10000 auth_mechanism: username: password: linkis_hive: host: 127.0.0.1 port: 9001 hdfs: name_node: hdfs://fate-cluster path_prefix: rabbitmq: host: 192.168.0.1 mng_port: 15672 port: 5672 user: fate password: fate route_table: mode: replication max_message_size: 1048576 pulsar: host: 192.168.0.1 port: 6650 mng_port: 18080 cluster: standalone tenant: fl-tenant topic_ttl: 5 route_table: mode: replication max_message_size: 1048576 nginx: host: 192.168.0.1 http_port: 9300 grpc_port: 9310 fateboard: host: 192.168.0.1 port: 8080 enable_model_store: false model_store_address: storage: mysql name: fate_flow user: fate passwd: fate_dev host: 127.0.0.1 port: 3306 max_connections: 10 stale_timeout: 10 servings: hosts: - 127.0.0.1:8000 fatemanager: host: 127.0.0.1 port: 8001 federatedId: 0 EOF
Modify and execute under the target server (192.168.0.2) app user¶
cat > /data/projects/fate/conf/service_conf.yaml <<EOF use_registry: false use_deserialize_safe_module: false dependent_distribution: false encrypt_password: false encrypt_module: fate_arch.common.encrypt_utils#pwdecrypt private_key: party_id: hook_module: client_authentication: fate_flow.hook.flow.client_authentication site_authentication: fate_flow.hook.flow.site_authentication permission: fate_flow.hook.flow.permission hook_server_name: authentication: client: switch: false http_app_key: http_secret_key: site: switch: false permission: switch: false component: false dataset: false fateflow: host: 192.168.0.2 http_port: 9380 grpc_port: 9360 nginx: host: http_port: grpc_port: proxy: nginx protocol: default database: name: fate_flow user: fate passwd: fate_dev host: 192.168.0.2 port: 3306 max_connections: 100 stale_timeout: 30 zookeeper: hosts: - 127.0.0.1:2181 use_acl: false user: fate password: fate default_engines: computing: spark federation: pulsar storage: localfs fate_on_standalone: standalone: cores_per_node: 20 nodes: 1 fate_on_eggroll: clustermanager: cores_per_node: 16 nodes: 1 rollsite: host: 127.0.0.1 port: 9370 fate_on_spark: spark: home: cores_per_node: 20 nodes: 1 linkis_spark: cores_per_node: 20 nodes: 2 host: 127.0.0.1 port: 9001 token_code: MLSS python_path: /data/projects/fate/python hive: host: 127.0.0.1 port: 10000 auth_mechanism: username: password: linkis_hive: host: 127.0.0.1 port: 9001 hdfs: name_node: hdfs://fate-cluster path_prefix: rabbitmq: host: 192.168.0.2 mng_port: 15672 port: 5672 user: fate password: fate route_table: mode: replication max_message_size: 1048576 pulsar: host: 192.168.0.2 port: 6650 mng_port: 18080 cluster: standalone tenant: fl-tenant topic_ttl: 5 route_table: mode: replication max_message_size: 1048576 nginx: host: 192.168.0.2 http_port: 9300 grpc_port: 9310 fateboard: host: 192.168.0.1 port: 8080 enable_model_store: false model_store_address: storage: mysql name: fate_flow user: fate passwd: fate_dev host: 127.0.0.1 port: 3306 max_connections: 10 stale_timeout: 10 servings: hosts: - 127.0.0.1:8000 fatemanager: host: 127.0.0.1 port: 8001 federatedId: 0 EOF
##### 6.3.5 mq route table configuration
**conf/rabbitmq_route_table.yaml**
```yaml
10000:
Host: 192.168.0.1
port. 5672
9999:
Host: 192.168.0.2
port. 5672
conf/pulsar_route_table.yaml
9999:
# host can be a domain name, e.g. 9999.fate.org
host: 192.168.0.2
port. 6650
sslPort: 6651
# Set proxy address for this pulsar cluster
proxy.""
10000:
# The host can be a domain name, such as 10000.fate.org
host: 192.168.0.1
port: 6650
sslPort: 6651
proxy.""
default.
# Compose hosts and proxies for parties that do not exist in the routing table
# In this example, the host for the 8888 party will be 8888.fate.org
proxy." proxy.fate.org:443"
Domain." fate.org"
port. 6650
sslPort: 6651
6.3.6 Nginx routing configuration file modification¶
configuration file : /data/projects/fate/proxy/nginx/conf/route_table.yaml
This configuration file is used by Nginx to configure routing information. You can manually configure it by referring to the following example, or you can use the following commands to complete:
#Modify and execute under the app user of the target server (192.168.0.1)
cat > /data/projects/fate/proxy/nginx/conf/route_table.yaml << EOF
default:
proxy:
- host: 192.168.0.2
http_port: 9300
grpc_port: 9310
10000:
proxy:
- host: 192.168.0.1
http_port: 9300
grpc_port: 9310
fateflow:
- host: 192.168.0.1
http_port: 9380
grpc_port: 9360
9999:
proxy:
- host: 192.168.0.2
http_port: 9300
grpc_port: 9310
fateflow:
- host: 192.168.0.2
http_port: 9380
grpc_port: 9360
EOF
#Modify and execute under the app user of the target server (192.168.0.2)
cat > /data/projects/fate/proxy/nginx/conf/route_table.yaml << EOF
default:
proxy:
- host: 192.168.0.1
http_port: 9300
grpc_port: 9310
10000:
proxy:
- host: 192.168.0.1
http_port: 9300
grpc_port: 9310
fateflow:
- host: 192.168.0.1
http_port: 9380
grpc_port: 9360
9999:
proxy:
- host: 192.168.0.2
http_port: 9300
grpc_port: 9310
fateflow:
- host: 192.168.0.2
http_port: 9380
grpc_port: 9360
EOF
7. Start the service¶
execute under the target server (192.168.0.1 192.168.0.2) app user
## Start FATE service, FATE-Flow depends on MySQL to start
Source code /data/projects/fate/bin/init_env.sh
cd /data/projects/fate/fateflow/bin
bash service.sh start
#Start the fateboard service
cd /data/projects/fate/fateboard
bash service.sh start
#Start the nginx service
/data/projects/fate/proxy/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /data/projects/fate/proxy/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
8. Fate client and Fate test configuration¶
Execute under the target server (192.168.0.1 192.168.0.2) app user
#Configure the fate client
source /data/projects/fate/bin/init_env.sh
flow init -c /data/projects/fate/conf/service_conf.yaml
#192.168.0.1 Execution:
pipeline init --ip 192.168.0.1 --port 9380
#192.168.0.2 Execution:
pipeline init --ip 192.168.0.2 --port 9380
#Configure the fate test
source /data/projects/fate/bin/init_env.sh
fate_test config edit
#192.168.0.1 parameters are modified as follows
data_base_dir: /data/projects/fate
fate_base: /data/projects/fate/fate
parties:
guest: [10000]
- flow_services:
- {address: 192.168.0.1:9380, parties: [10000]}
#192.168.0.2 parameters are modified as follows
data_base_dir: /data/projects/fate
fate_base: /data/projects/fate/fate
parties:
guest: [9999]
- flow_services:
- {address: 192.168.0.2:9380, parties: [9999]}
9. Problem location¶
1) FATE-Flow log
/data/projects/fate/fateflow/logs
2) FATE-Board logs
/data/projects/fate/fateboard/logs
3) Nginx logs
/data/projects/fate/proxy/nginx/logs
10. Testing¶
10.1 Verify toy example Deployment¶
A user must set 2 parameters for this testing: gid(guest partyid), hid(host partyid).
10.1.1 One-Sided Testing¶
1) Execute on 192.168.0.1, with both gid and hid set to 10000:
source /data/projects/fate/bin/init_env.sh
flow test toy -gid 10000 -hid 10000
A result similar to the following indicates successful operation:
"2020-04-28 18:26:20,789 - secure_add_guest.py[line:126] - INFO: success to calculate secure_sum, it is 1999.9999999999998"
Tip: If the error "max cores per job is 1, please modify job parameters" appears, a user needs to modify the parameter task_cores to 1, add "--task-cores 1" to run toy test.
2) Execute on 192.168.0.2, with both gid and hid set to 9999:
source /data/projects/fate/bin/init_env.sh
flow test toy -gid 9999 -hid 9999
A result similar to the following indicates successful operation:
"2020-04-28 18:26:20,789 - secure_add_guest.py[line:126] - INFO: success to calculate secure_sum, it is 1999.9999999999998"
10.1.2 Two-Sided Testing¶
Select 9999 as the guest and execute on 192.168.0.2:
source /data/projects/fate/bin/init_env.sh
flow test toy -gid 9999 -hid 10000
A result similar to the following indicates successful operation:
"2020-04-28 18:26:20,789 - secure_add_guest.py[line:126] - INFO: success to calculate secure_sum, it is 1999.9999999999998"
10.2 Minimization Testing¶
10.2.1 Upload Preset Data:¶
Execute on 192.168.0.1 and 192.168.0.2 respectively:
source /data/projects/fate/bin/init_env.sh
fate_test data upload -t min_test
10.2.2 Fast Mode:¶
Ensure that both the guest and host have uploaded the preset data with the given script.
In fast mode, the minimization testing script will use a relatively small breast dataset containing 569 pieces of data.
Select 9999 as the guest and execute on 192.168.0.2:
source /data/projects/fate/bin/init_env.sh
#One-sided testing
flow test min -gid 9999 -hid 9999 -aid 9999 -t fast
#Two-sided testing
flow test min -gid 9999 -hid 10000 -aid 10000 -t fast
Other parameters that may be useful include:
- -f: The file type used. Here, "fast" represents the breast dataset, and "normal" represents the default credit dataset.
- --add_sbt: When set to 1, the secureboost task will start after running lr. When set to 0, the secureboost task will not start. When not set, this parameter will default to 1.
The word "success" will display in the result after a few minutes to indicate the operation has been completed successfully. If "FAILED" appears or the program gets stuck, it means that the test has failed.
10.2.3 Normal Mode:¶
Just replace "fast" with "normal" in the command. All other parts are identical to fast mode.
10.3 Fateboard Testing¶
Fateboard is a web service. When started, it allows a user to view task information by visiting http://192.168.0.1:8080 and http://192.168.0.2:8080. If there is a firewall, a user needs to turn it on.
11. System Operation and Maintenance¶
================
11.1 Service Management¶
execute under the target server (192.168.0.1 192.168.0.2) app user
11.1.1 FATE Service Management¶
1) Start/shutdown/view/restart the fate_flow service
source /data/projects/fate/init_env.sh
cd /data/projects/fate/fateflow/bin
bash service.sh start|stop|status|restart
If you start module by module, you need to start eggroll first and then fateflow. fateflow depends on eggroll to start.
2) Start/shutdown/restart FATE-Board service
cd /data/projects/fate/fateboard
bash service.sh start|stop|status|restart
3) Start/shutdown/restart the NginX service
cd /data/projects/fate/proxy
./nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
./nginx/sbin/nginx -s stop
11.1.2 MySQL Service Management¶
Start/shutdown/view/restart MySQL services
cd /data/projects/fate/common/mysql/mysql-8.0.13
bash ./service.sh start|stop|status|restart
11.2 Viewing processes and ports¶
execute under the target server (192.168.0.1 192.168.0.2) app user
11.2.1 View processes¶
# Check if the process is started according to the deployment plan
ps -ef | grep -i fate_flow_server.py
ps -ef | grep -i fateboard
ps -ef | grep -i nginx
11.2.2 Viewing process ports¶
### 8.2.2 Checking the process ports according to the deployment plan
### 8.2.2 Checking process ports
netstat -tlnp | grep 9360
#fateboard
netstat -tlnp | grep 8080
#nginx
netstat -tlnp | grep 9390
11.3 Service logs¶
| service | logpath |
|---|---|
| fate_flow&task_logs | /data/projects/fate/fateflow/logs |
| fateboard | /data/projects/fate/fateboard/logs |
| nginx | /data/projects/fate/proxy/nginx/logs |
| mysql | /data/projects/fate/common/mysql/mysql-*/logs |