English | 中文
FATE FLOW¶
Introduction¶
FATE-Flow is the job scheduling system of the federated learning framework FATE, which realizes the complete management of the federated learning job life cycle, including data input, training job scheduling, indicator tracking, model center and other functions
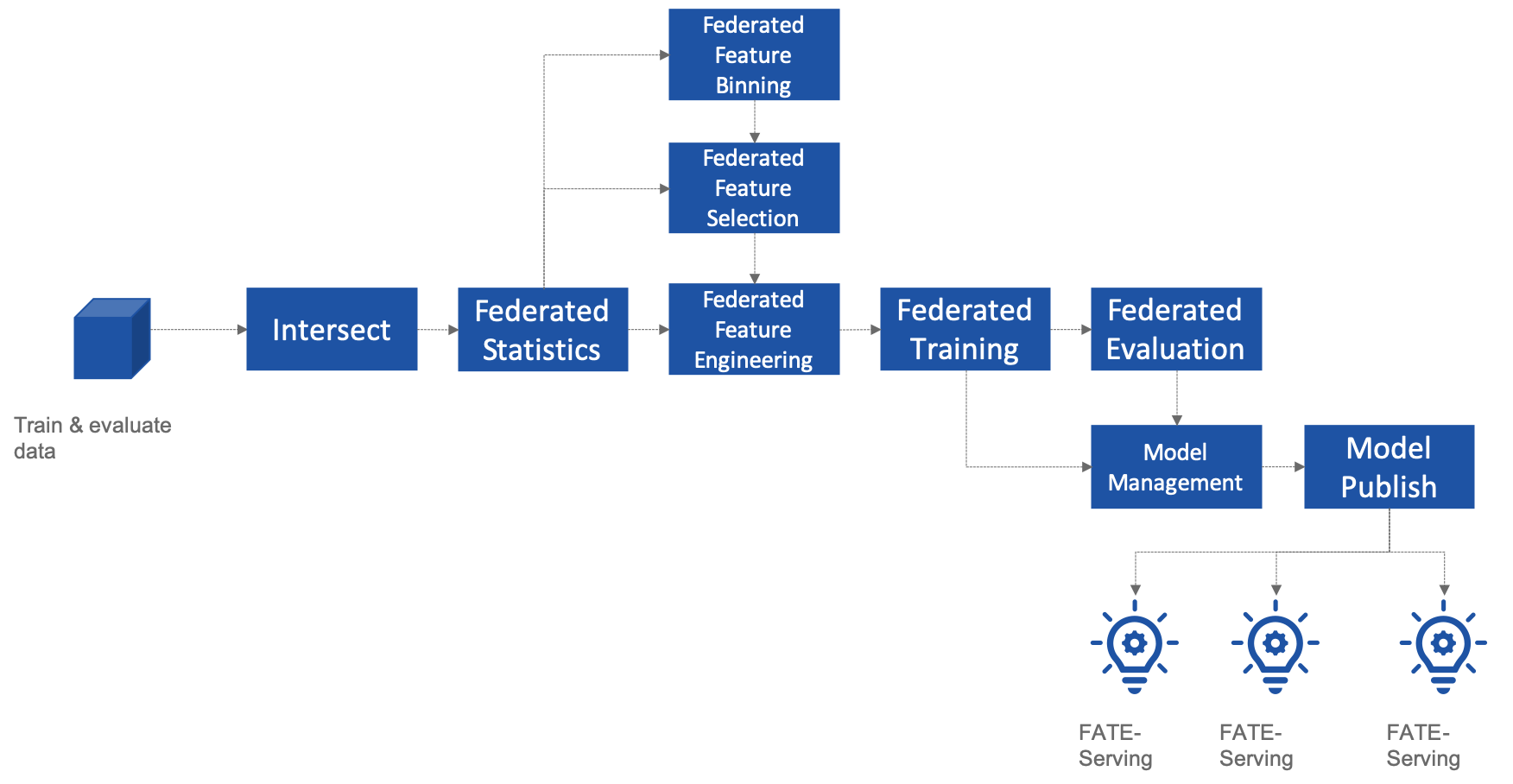 FATE-Flow Federated Learning
Pipeline{.align-center}
FATE-Flow Federated Learning
Pipeline{.align-center}
FATE-Flow now supports¶
DAG define Pipeline
Describe DAG using FATE-DSL in JSON format
Advanced scheduling framework, based on global state and optimistic lock scheduling, single-party DAG scheduling, multi-party coordinated scheduling, and support for multiple schedulers
Flexible scheduling strategy, support start/stop/rerun, etc.
Fine-grained resource scheduling capabilities, supporting core, memory, and working node strategies based on different computing engines
Realtime tracker, real-time tracking data, parameters, models and indicators during operation
Federated Learning Model Registry, model management, federated consistency, import and export, migration between clusters
Provide CLI, HTTP API, Python SDK
Architecture¶
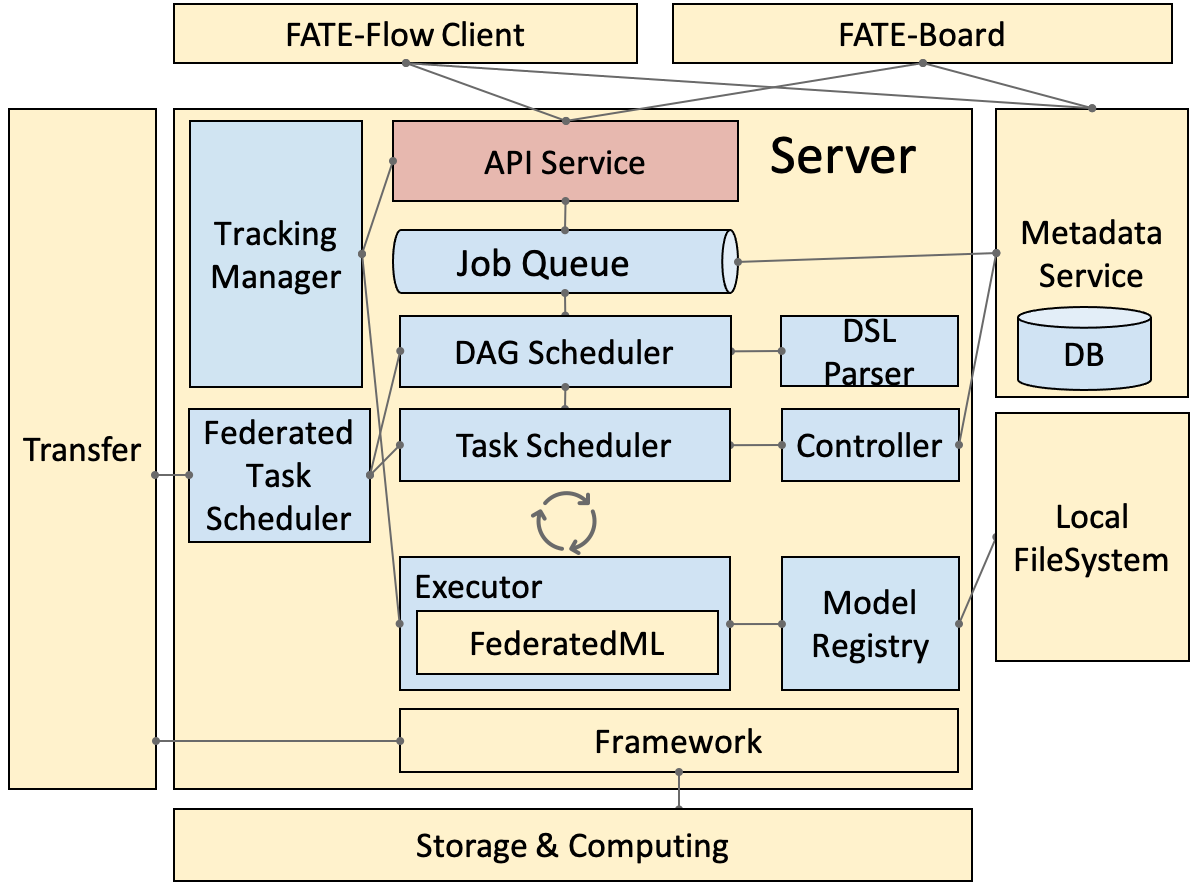 fateflow_arch{.align-center}
fateflow_arch{.align-center}
Usage¶
FAQ¶
What is the role of FATE FLOW in the FATE?
:
FATE Flow is a scheduling system that schedules the execution of algorithmic components based on the DSL of the job submitted by the user.
ModuleNotFoundError
: No module named “arch”:
Set PYTHONPATH to the parent directory of fate_flow.
Why does the task show success when submitting the task, but the task fails on the dashboard page?
:
Submit success just means that the job was submitted and not executed. If the job fails, you need to check the log.
You can view the logs through the board.
What meaning and role do the guest, host, arbiter, and local roles represent in fate?
:
Arbiter is used to assist multiple parties to complete joint modeling. Its main role is to aggregate gradients or models. For example, in vertical lr, each party sends half of its gradient to arbiter, and then arbiter jointly optimizes, etc.
Guest represents the data application party.
Host is the data provider.
Local refers to local, only valid for upload and download.
Error about”cannot find xxxx” when killing a waiting job
:
Fate_flow currently only supports kill on the job initiator, kill will report “cannot find xxx”.
What is the upload data doing?
:
Upload data is uploaded to eggroll and becomes a DTable format executable by subsequent algorithms.
How to download the generated data in the middle of the algorithm?
:
You can use
:
python fate_flow_client.py -f component_output_data -j $job_id -r $role -p $party_id -cpn $component_name -o $output_path
If the same file upload is executed twice, will fate delete the first data and upload it again?
:
It will be overwritten if the keys are the same in the same table.
What is the reason for the failure of this job without error on the board?
:
The logs in these places will not be displayed on the board:
$job_id/fate_flow_schedule.log,logs/error.log,logs/fate_flow/ERROR.log.
What is the difference between the load and bind commands?
:
Load can be understood as a model release, and bind is the default model version.